How to trade Forex
Leverage, volume, required margin
Balance, equity, free margin, margin level
Pros and cons of trading Forex
Forex is like a big marketplace where people buy and sell different currencies from around the world, such as dollars, euros, pounds, or yen. For instance, if you believe the euro will increase in value relative to the dollar, you might exchange your dollars for euros now and later sell those euros for more dollars once their value has risen. This whole process happens all over the world. Indeed, Forex is the biggest money market out there, with people trading trillions of dollars every single day. In the Forex market, you’ll see that not only regular people trade but also banks and big companies that are trying to make money by forecasting how currency values will change. So, it’s a mix of market analysis and strategy to try to earn profits from these currency exchanges. Currencies are bought and sold in pairs, like the U.S. dollar and the euro (EURUSD) or the British pound and the Japanese yen (GBPJPY). Traders try to forecast which currency will get stronger or weaker compared to the other. They buy a currency that they think will go up in value compared to the one they are selling.What is Forex trading
The Forex market is open 24 hours a day, five days a week. It operates in different parts of the world in different time zones, so you can trade almost whenever you want. To trade, people use brokers, who act as middlemen, to help them buy and sell currencies. These brokers have special platforms, apps or websites, where traders can easily place their orders. The prices of currencies change based on how many people want to buy or sell them. This is called supply and demand. Things like economic news, political events, or decisions made by banks can all affect these prices. So, if a lot of people want to buy a currency, its price goes up; if not many people want it, the price goes down.How the Forex market works
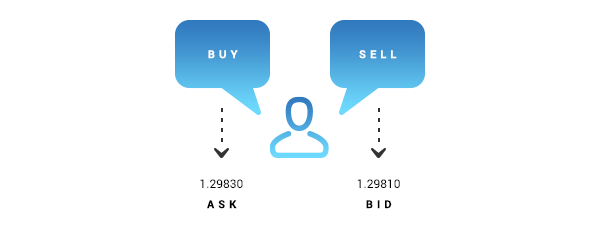
Enjoying this article? Download the key points as a PDF (in English). Let’s take a look at some basic Forex terms: Currency pairs. In Forex, you always trade two currencies together, like EURUSD (euro and U.S. dollar). The first one is what you’re buying (base currency), and the second is what you’re selling (quote currency). The quoted price tells you how much of the quote currency is required to purchase one unit of the base currency. Pips. A pip is a small unit of measurement that represents a minor change in a currency's price. In most currency pairs, prices are quoted to four decimal places, and a pip refers to a movement of 0.0001. Leverage. Leverage lets you control a large amount of money with only a small initial investment. For example, if you have a 100:1 leverage, you can control $10,000 with just $100. Leverage can amplify your potential profits, but may also make you lose money faster. Bid and ask price. The bid price is what you get when you sell your currency, and the ask price is what you pay when you buy it. The ask price is higher than the bid and the difference between these two prices is called the spread. For example, if the bid price is 1.11443 and the ask price is 1.11449, the spread is 0.6 pips.Forex basics
Market orders and limit orders. A market order means you buy or sell right away at the current price. A limit order means you set a specific price at which you want to buy or sell.
Technical and fundamental analysis. Technical analysis is about looking at price charts to predict where prices might go next. Fundamental analysis focuses on things like interest rates and job reports to understand how strong a currency really is.
Trading sessions. The Forex market is open 24 hours on weekdays, divided into different time zones (Asian, European, and North American). At each time of the day, there are different levels of activity. A trading session refers to the hours when the most trading happens in each major region.
Risk management. Managing risk is incredibly important. This means setting limits on how much money you can afford to lose on a trade, should the market turn against you, and not risking too much of your total capital on a single trade.
Demo accounts. Many trading platforms let you practise on demo accounts which don’t use real money. This is a great way to learn how to trade Forex without risking real cash.
Brokerage accounts. To trade Forex, you need to sign up with a broker, which acts like a middleman. Make sure to choose one that’s trustworthy and has a convenient trading platform.
Further, we will explore some of the elements of the Forex market in more detail so that you can learn to trade Forex.
All currencies in Forex trading are quoted in pairs, one against another. Their names are given as a three-letter abbreviation known as an ISO code, where the first two letters represent the country and the third one is the name of the currency. Depending on how commonly they are traded, currencies can be divided into three categories: The most traded ones are usually referred to as majors and include the U.S. dollar, the euro, the Great Britain pound, the Japanese yen, the Canadian dollar, the Swiss franc, the Australian dollar, and the New Zealand dollar. Major pairs are between the U.S. dollar and one of the other currencies from the list above, for example EURUSD, USDJPY, and USDCHF. Cross pairs consist of two major currencies, neither of which is the U.S. dollar, such as EURGBP, EURCHF, EURJPY, GBPCAD, GBPAUD, and CHFJPY. Exotic pairs consist of a major currency and another less traded one, for instance, EURTRY, USDSEK, USDDKK, USDHDK, and USDSDG. Exotics tend to be less liquid, meaning, they are harder to buy or sell and have wider spreads. You may also want to read: How to start trading in 4 easy steps, An introduction to Forex Market.Currency pairs and rates
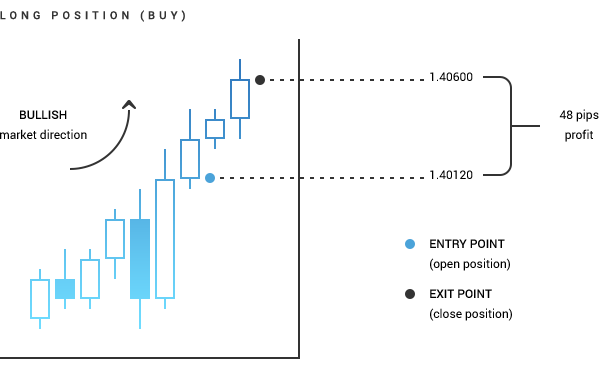
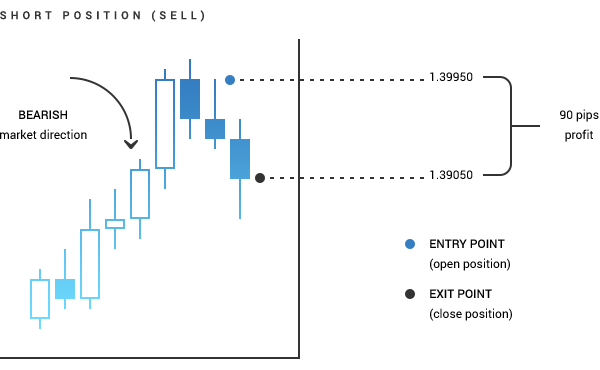
Direction wise, there are two types of trades: buy, or long, positions that are opened at the ask price and closed at the bid price sell, or short, positions that are opened at the bid and closed at the ask price. Each of these can be opened either as a market or as a pending order: Direction Market Pending Stop Limit Long (buy) Opened at current ask price Opened at a predefined ask price, which is above the current one Opened when the ask price reaches the order level; the current ask is below this price Short (sell) Opened at current bid price Opened at a predefined bid price, which is below the current one Opened at a predefined bid price, which is above the current one A closing order is always the reverse of the opening order. When you close a long (buy) position, you sell the amount back. Similarly, when you close a short (sell) position, you buy back the amount you initially sold. A position can either be closed manually at the current market rate or when a certain price level is reached, through stop-loss and take-profit orders. Stop loss is intended to limit potential losses and is set above the open price for short positions and below the open price for long positions. Take profit allows you to close a position when a certain profit is gained. The take profit level should be set below the current ask price for a short position and above the current bid price for a long position. In order to gain profit, you need to close long positions when the price goes up and short positions when the price goes down.Orders
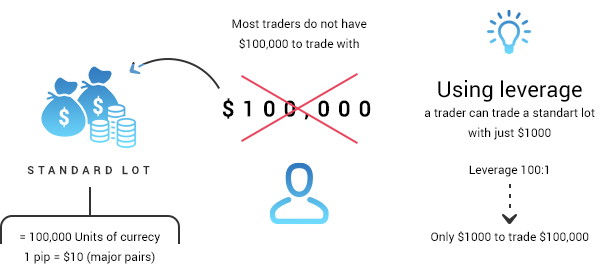
To open a position, you need to have a certain amount in your balance, which is commonly referred to as required margin or just margin. The amount needed depends on the trading instrument, volume, and leverage. Trading instruments are essentially anything you can trade, including currency pairs, metals, oil, or indices. Volume is the amount you buy or sell measured in lots. One standard lot equals 100,000 units of the base currency. Depending on your balance and account type, you can also trade mini lots (0.1) and micro lots (0.01). Volume defines the pip price, that is, the higher your volume is, the more significant each price movement will be. For example, the pip price for one lot of EURUSD is 10 USD, and for 0.5 lots of EURUSD is 5 USD. You can use this tool to calculate pip price for any position. Leverage is a virtual credit provided by the broker. The higher your leverage is, the lower your marginal requirements will be. For example, when you use no leverage (ratio 1:1), you will need 100,000 EUR to open an order for 1 lot of EURUSD; if your account leverage is 1:200, only 500 EUR will be required. The maximum leverage Octa offers is 1:1000, that is, you will need only 100 EUR to open an order for 1 lot.Leverage, volume, and required margin
Note that if you have a USD account, the required margin will be calculated as follows:
(Current price × Volume in lots × 100 000 units) / leverage
For example, if your leverage is 1:200 and you open 0.5 lot EURUSD order at 1.12931, required margin is
(1.12931 × 0.5 lots × 100 000 units) / 200 = 282.33 USD
Required margin is always calculated automatically by the platform. To check how much money approximately will be required to open a certain position, you can use our Forex Calculator.
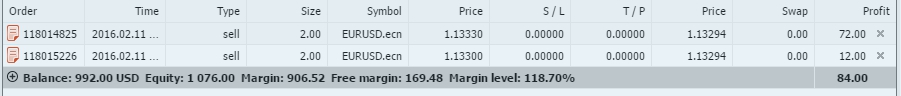
When you open a position, note that your balance remains intact. In fact, it only includes deposits, withdrawals, and closed trades. The amount of required margin will be deducted from the 'Free margin' field, which also comprises your floating profit or loss and deposit bonus if you claimed one. Free margin is the funds you can open positions with. Note that when you open a hedge order with the same volume, no margin will be required; however, if your free margin is negative, you will not be able to open an opposite position. Free margin = balance – required margin + floating profit / loss (+ deposit bonus) Another value affected by your profit or loss is equity, which is calculated as follows: Equity = balance + floating profit / loss (+ deposit bonus) Equity is important because, along with the required margin, it determines your margin level: Margin level = equity / required margin × 100% If your margin level falls under 15%, your open positions will be mandatory closed starting with the trade that has the highest floating loss. Balance, equity, free margin, and margin level are calculated automatically by the platform and are available anytime in the 'Trade' tab.Balance, equity, free margin, and margin level
Let's say the exchange rate for EURUSD is 1.09140/1.09180 (buying/selling). This rate shows how many U.S. dollars you can exchange for one euro. You believe the euro will strengthen against the dollar, so you decide to buy €20,000. With a margin rate of 0.5%, you only need to deposit a small fraction of the total trade value. The total value of your trade is €20,000 x 1.09180 = $21,836. With a 0.5% margin requirement, you only need to deposit $109.18 to open the position. Your prediction was correct. The price moves up, and the selling price (bid) rises to 1.09680. You decide to close your position by selling at the higher price. The price moved up by 50 pips (1.09680 - 1.09180). To calculate your profit: Unfortunately, the market moved against you, and the price dropped. The selling price (bid) falls to 1.08680. To minimize your losses, you decide to sell at this lower price. The price moved down by 50 pips (1.09180 - 1.08680). To calculate your loss: Bid/Ask Spread: The bid (1.09140) is the price you can sell at, while the ask (1.09180) is the price you buy at. Pip Movement: A change of 50 pips (0.00050) resulted in a $100 profit or loss based on a €20,000 trade. Margin: With 0.5% margin, you only need to deposit a fraction of the full trade value.Forex trading example: buying EURUSD
Option A: profit scenario
€20,000 x 1.09680 = $21,936
€20,000 x 1.09180 = $21,836
Your profit is $21,936 - $21,836 = $100.Option B: loss scenario
€20,000 x 1.08680 = $21,736
€20,000 x 1.09180 = $21,836
Your loss is $21,736 - $21,836 = -$100.Key Points:
Pros Cons Trade anytime. You can trade whenever you want during the week. The market is open 24 hours from Monday to Friday, so you can jump in at almost any time. Market unpredictability. The Forex market moves quickly, creating exciting opportunities for traders but with chances to lose money. Without proper risk management and strategy, there is always a risk of losses. However, with the right knowledge and practice, you can take advantage of these movements. Your schedule. You get to choose how much time you want to spend on trading. It’s all up to you. The need for dedicated studying. The fast-moving market can present great opportunities, but without proper knowledge and preparation, it’s easy to make costly mistakes. Taking the time to understand strategies, market trends, and risk management is essential for long-term success. Borrowing money. You can use margin trading where you borrow money from your broker to trade a larger amount. This gives you a higher profit potential. Higher risks with margin trading. When you borrow money and trade with a larger amount, it can help you make more profit. But it also means you could lose a lot more if things go wrong. Career potential. If you really understand how the market works, trading could even become a full-time job for you. High expectations. Forex is often advertised in a way that makes it sound super easy and profitable. Many people think they’ll get rich quickly and get upset when they don’t see immediate results. However, consistent learning is key.Pros and cons of trading Forex
All you need to do to start trading Forex is to open an account on our website or download the Octa trading app. Demo account allows you to practise risk free, without using real funds, while with a real account, you will be able to experience the real market with a minimum deposit. Find more information on how the Forex market works, what tools and techniques you can employ, or strategies you can apply in the Forex Basics section of our website. If you have any questions regarding the market, the Octa website, or trading conditions, you can check our comprehensive FAQ. Whenever you encounter an unfamiliar term, word or market phenomenon, you can check its definition and description in the Forex Glossary. Our award-winning 24/7 Customer Service will be more than happy to answer any questions you may have. How to start trading
Forex trading is essentially exchanging currencies from different countries. Trading is done in pairs, such as the euro and the dollar, and you try to make money by forecasting how their values will change. If you think one currency will get more valuable, you buy it. If you think it will lose value, you sell it. Traders use tools like charts that show price changes, as well as economic news and updates to help them decide when to buy or sell. It’s necessary to keep in mind that while you can make money, there’s also a risk of losing it, so studying Forex trading strategies and keeping up-to-date on market news is essential. With Octa Space, a live feed with the latest trading ideas right in the OctaTrader trading platform, even beginner traders can better understand the market and make their first trades.Final thoughts





